The Impact of FTX’s Bankruptcy on the Ethereum Price
General information
- Author: Haowen Ji, Data Science, Class 2023, Duke Kunshan University
- Instructor: Prof. Luyao Zhang, Duke Kunshan University
- Disclaimer: Submissions to the final project for STATS201 Introduction to Machine Learning for Social Science, 2023 Spring Term (Seven Week - First) instructed by Prof. Luyao Zhang at Duke Kunshan University.
- Acknowledgments: I would like to thank Prof. Luyao Zhang for her instructions on STATS201 and thanks all the classmates for the inspiring discussions and feedbacks.
Project Summary
1. Explanation project:
- Background & Motivation: Cryptocurrencies have emerged as a popular investment and payment option in recent years, and the cryptocurrency market has grown rapidly (Canh, Binh, and Thanh 2019). However, the volatility of cryptocurrency prices has posed significant challenges for stakeholders. As a result, there is a growing interest in the development of accurate and reliable cryptocurrency price prediction models to assist investors in making informed decisions. The development of cryptocurrency price prediction models is challenging due to the complexity and unpredictability of the cryptocurrency market (Ametrano 2014). One approach to improving cryptocurrency price prediction is using an explanation, which involves identifying the key factors that drive cryptocurrency prices. The explanation provides a more transparent and interpretable approach to price prediction.
- Research Question: What are the hot topics in the cryptocurrency price prediction field?
- Application Scenarios: This project is applied to 12 papers related to the cryptocurrency price prediction. These papers are collected by keyword searching in google scholar, and their titles and abstracts are used for the natural language processing (Ritchie 1982) task.
- Methodology: The machine learning methodology explanation is used in this project. To conduct text analysis, the project employs both word cloud and bigram approaches. These methods enable a deeper understanding of the text data and provide valuable insights for the project.
- Results: The word cloud shows that when it comes to predicting cryptocurrency prices, the most popular digital currencies used for this task are Bitcoin and Ethereum. Additionally, we noticed that machine learning methods are commonly used for this type of prediction, and there is a lot of interest in time-series forecasting techniques. Overall, these findings suggest that those looking to predict cryptocurrency prices should focus on these two currencies and consider utilizing machine learning and time-series analysis techniques.
- Intellectual Merit & Practical Impacts: The study contributes to the transparency and interpretability of cryptocurrency price prediction tasks. The study’s results and implications can inform the development of more effective cryptocurrency price prediction models, ultimately assisting investors in making informed decisions in a volatile market. For future work, more literature can be collected to generate more robust results and more sophisticated explanation models that integrate both quantitative and qualitative data can be developed to enhance the transparency and interpretability of cryptocurrency price prediction models.
2. Prediction project:
- Background & Motivation: Ethereum is a decentralized digital currency that has attracted significant attention due to its high market capitalization and potential for decentralized applications. Accurately predicting the price of Ethereum is critical for stakeholders in the cryptocurrency market to make informed decisions and minimize risks (S, Mohta, and Rangaswamy 2022). However, developing accurate and reliable price prediction models for Ethereum is challenging due to the complexity and unpredictability of the cryptocurrency market. This study aims to investigate the machine learning methods and develop accurate and reliable price prediction models for Ethereum.
- Research Question: How effective are machine learning algorithms in predicting Ethereum closing price?
- Application Scenarios:: This project is applied to the Ethereum closing price from 2015 to 2021. The data is downloaded from Ethereum (ETH-USD) Historical Dataset(Kaggle). The closing price is chosen to represent the Ethereum price. The date is the x variable, and it ranges from 2015/8/7 to 2021/10/20. The Y variable is the closing price of Ethereum, which ranges from 0.434829 to 4168.701172.
- Methodology: The machine learning methodology prediction is used in this project. Two machine learning algorithms to develop price prediction models for Ethereum closing price: linear regression and random forest regression. The linear regression is used to build a simple and interpretable model that could capture the linear relationship between Ethereum’s closing price and its predictors. Random forest regression is used to build a more complex model that could capture nonlinear relationships and interactions between features.
- Results: The performance of linear regression and random forest regression models in predicting the Ethereum closing prices was evaluated using the coefficient of determination (R-squared or R2)(Lee et al. 2012). Linear regression had a good performance in predicting Ethereum’s closing price, with an R2 score of 0.985. This indicates that 98.5% of the variance in Ethereum closing price can be explained by the linear regression model. Random forest regression, on the other hand, was not efficient in predicting Ethereum closing price, with an R2 score of 0.393.
- Intellectual Merit & Practical Impacts: This research contributes to the field of cryptocurrency price prediction by evaluating the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms in predicting Ethereum’s closing price. This research has practical implications for stakeholders in the cryptocurrency market since it provides insights into the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms for predicting cryptocurrency prices and can help investors make decisions and minimize risks. Future work in this research could investigate the use of deep learning algorithms for predicting Ethereum closing price and explore the potential of incorporating external factors, such as news sentiment and social media data, into prediction models.
3. Causal inference project:
- Background & Motivation: In recent years, the popularity of cryptocurrencies as a means of investment and payment has increased significantly. However, the potential risks associated with these new financial systems, including bankruptcy, have not been fully understood. Bankruptcy, a common occurrence in centralized finance, can have significant impacts on the price and other aspects of financial systems (Devi and Radhika 2018). However, little research has been done to investigate the impact of bankruptcy on the cryptocurrency market (Abdillah and Hendrawan 2022). To address this research gap, I investigate the impact of the Futures Exchange (FTX) bankruptcy on the price of Ethereum, a popular decentralized digital asset. FTX is a representative example of cryptocurrency derivatives exchanges, which are relatively new and rapidly growing. Ethereum is chosen because of its decentralized nature (Zhang, Ma, and Liu 2022), which offers insights into the risks and opportunities of decentralized finance and cryptocurrencies. My study aims to contribute to a better understanding of the impact of bankruptcy on the cryptocurrency market and inform stakeholders of the potential risks and opportunities of investing in these new financial systems.
- Research Question: What is the causal relationship between the bankruptcy of FTX and the price of Ethereum?
- Application Scenarios: The data is extracted from Coin Metrics (Coin Metrics 2023). The data has two attributes, the first one is the date and the second is the closing price of Ethereum corresponding to each day in the unit ETH / USD. The date is the x variable, and it ranges from 2015/8/8 to 2023/2/23. The Y variable is the closing price of Ethereum, which ranges from 0.420000 to 4811.156463. The trend of the whole data is shown in Figure 1. It is obvious that the price of Ethereum has increased significantly overall since its release, but there has been a lot of fluctuation. The area between the orange line and the red line is the period of FTX bankruptcy. These two dates will be put into the regression discontinuity design as the representation of FTX bankruptcy separately.
- Methodology: The regression discontinuity is employed in this research, which is a statistical method commonly used to estimate the causal effects of an intervention on an outcome of interest. In this research, regression discontinuity can be examined whether there is a discontinuity in the trend of Ethereum prices at the time of FTX bankruptcy. The linear regression is used to fit separately the data from two groups: Ether price before and after FTX bankruptcy.
- Results: The results of the regression discontinuity analysis shows a clear discontinuity in the Ethereum price following the FTX bankruptcy. This finding is consistent with our prior expectations, suggesting that the FTX bankruptcy had a significant causal effect on the Ethereum price. Furthermore, it indicates a gradual increase in Ethereum price over time after the event, implying that the impact of the FTX bankruptcy is likely to have diminished over time.
- Intellectual Merit & Practical Impacts: The study presented in this paper contributes to the intellectual discourse surrounding the impact of bankruptcy on the cryptocurrency market, which has not been extensively explored in previous research. The findings of this study have important implications for stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and policymakers, who need to have a better understanding of the risks associated with these new financial systems. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of Ethereum, which is a focus of this study, offers insights into the risks and opportunities of decentralized finance and cryptocurrencies, which have the potential to transform the traditional financial system. There are several possible directions for future research based on the findings of this study. First, additional research could explore the effects of bankruptcy on other cryptocurrencies and decentralized financial systems with the methodology used in this research. Second, further research could investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the observed effects of bankruptcy on the price of Ethereum. Third, given the rapid evolution of the cryptocurrency market and decentralized finance, ongoing research is necessary to stay abreast of emerging risks and opportunities in this rapidly changing field.
Table of Contents
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Data | The data section of the three projects |
| Code | The code section of the three projects |
| Spotlight | Some spotlights of the three projects |
| More about the Author | More information about the author |
| References | References used in these projects |
Data
Data Source:
Meta Data Information
| Data files | Data Content | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Literatures.csv | Literatures collected for explanation | queried data |
| title_bigram.csv | The title biagram for the literatures collected | processed data |
| abstract_bigram.csv | The abstract biagram for the literatures collected | processed data |
| ETHUSD.csv | Ethereum historical data from 2015 to 2021 | queried data |
| Ethereum_value.csv | Ethereum data after preprocessing | processed data |
| Regression_Train.csv | Data for model training | processed data |
| Regression_Test.csv | Data for model test | processed data |
| Ethereum_Data.csv | The closing price of Ethereum from 2015 to 2023 | queried data |
Data Dictionary
| File Name | Variable Name | Description | Frecuency | Unit | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Literatures.csv | Title | The titles of 12 literatures related to cryptocurrency prediction | 1 | None | str |
| Abstract | The abstracts of 12 literatures related to cryptocurrency prediction | 1 | None | str | |
| title_bigram.csv | bigram | The biagram of titles | None | None | tuple |
| counts | The frequency of occurrence for each bigram | None | None | int | |
| abstract_bigram.csv | bigram | The abstract of abstracts bigram | None | None | tuple |
| counts | The frequency of occurrence for each bigram | None | None | int | |
| ETHUSD.csv | Date | The date of the collected data from 2015-08-07 to 2021-10-20 | daily | day | Object |
| Open | The opening price of the Ethereum | daily | USD | float | |
| Close | The closing price of the Ethereum | daily | USD | float | |
| Ethereum_value.csv | Date | The processed date time from ETHUSD | daily | day | datetime |
| Regression_Train.csv | 6-month-ma | The mean value of the closing price for the past 6 months | daily | USD | float |
| Regression_Test.csv | 6-month-ma | The mean value of the closing price for the past 6 months | daily | USD | float |
| Ethereum_Data.csv | ETH / USD Denominated Closing Price | The closing price of Ethereum from 2015-08-07 to 2021-10-20 | daily | USD | float |
Code
- Query Data for Explanation
- Query Data for Prediction
- Process Data for Prediction
- Analyze Data for Prediction
- Process and Analyze Data for Causal Inference
Table of Code
| Code files | Description | Type | Task | Emoji |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haowen_NLP_Explanation.ipynb | This code uses the NLP method to generate word cloud and bigram | .ipynb | Explanation | :page_with_curl: |
| Query_Ethereum_Data.ipynb | This code deals with the read and preprocessing of the original dataset | .ipynb | Prediction | :moneybag: |
| Process_Data_Prepare_X_and_Y_for_Regressions.ipynb | This code processed the X and Y dataset from Ethereum_value.csv for regression | .ipynb | Prediction | :tada: |
| Analyze_Data_Machine_Learning_for_Predicting.ipynb | This code applied machine learning method for open price regression | .ipynb | Prediction | :chart_with_upwards_trend: |
| Analyze_Data_Machine_Learning_for_Predicting.ipynb | This code applied the regression discontinuity method | .ipynb | Causal Inference | :paperclip: |
Spotlight
Poster
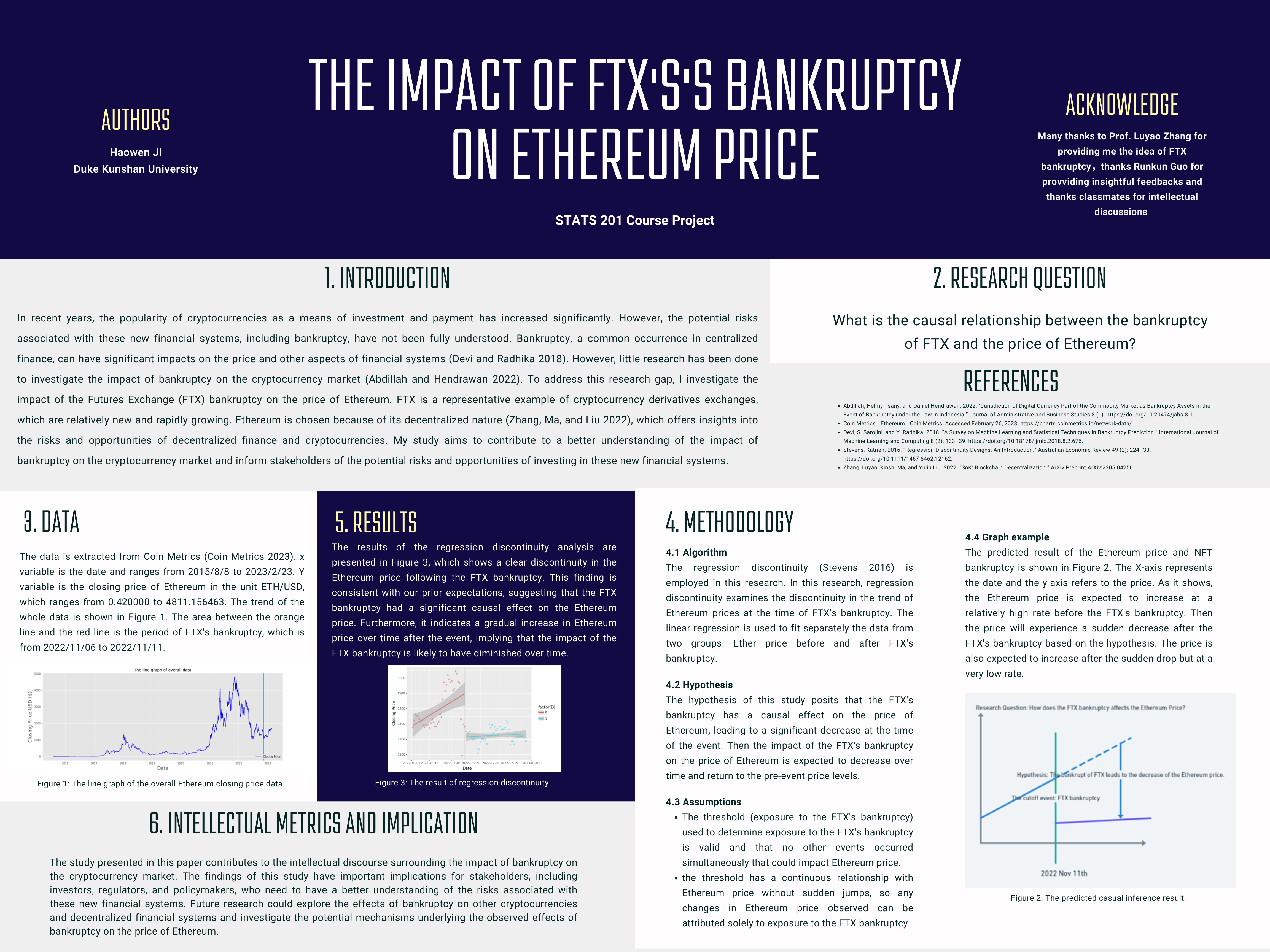
Figure 1: Poster of the final project
- The final version of the poster is shown in Figure 1. This poster gives an overview of causal inference research. It contains six sections: Introduction, Research Question, Data, Methodology, Results, Intellectual Metrics and Implication
- This poster is created by Canva
Explaination
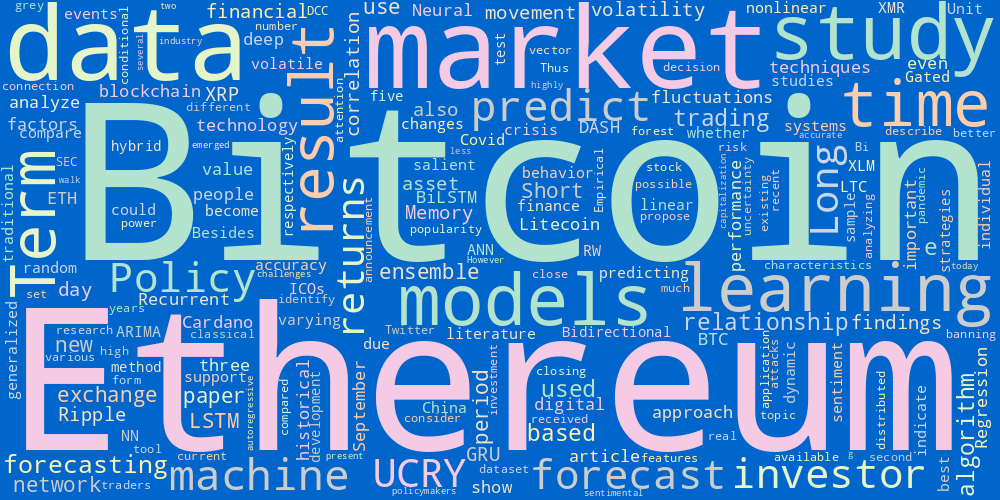
Figure 2: The word cloud of the literatures on the topic "Cryptocurrency Price Prediction"
- Code source
- Data source
- Description: This word cloud in Figure 2 is generated from the abstracts of 12 papers related to cryptocurrency price prediction. These literatures are collected by keyword searching in google scholar. It can be inferred that the most popular digital currencies used for this task are “Bitcoin” and “Ethereum”. Besides, “machine” and “learning” are also high-frequency words, which means this method is commonly used for this type of prediction, and the words “time” and “BiLSTM” shows that there is also some interest in time-series forecasting techniques.
Prediction
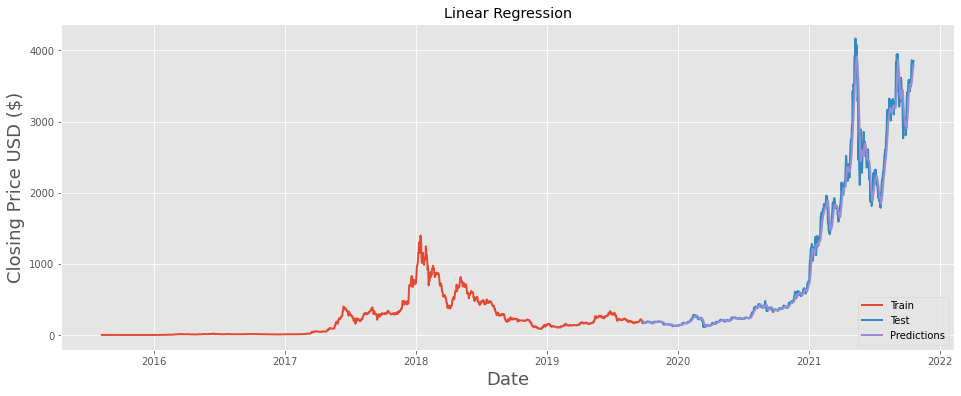
Figure 3: The prediction result of ethereum closing price by linear regression
- Code source
- Data source
- Description: Figure 3 is the linear regression prediction result of the Ethereum closing price. The x-axis represents the date, which ranges from 2015/8/7 to 2021/10/20. The y-axis is the closing price of Ethereum. The data was split in 3:2 in this task. The red curve in the figure is the training data. The purple curve is the prediction price by linear regression. It is very close to the actual data (the blue curve). Linear regression reached a good performance in predicting Ethereum’s closing price, with an R2 score of 0.985.
Causal Inference
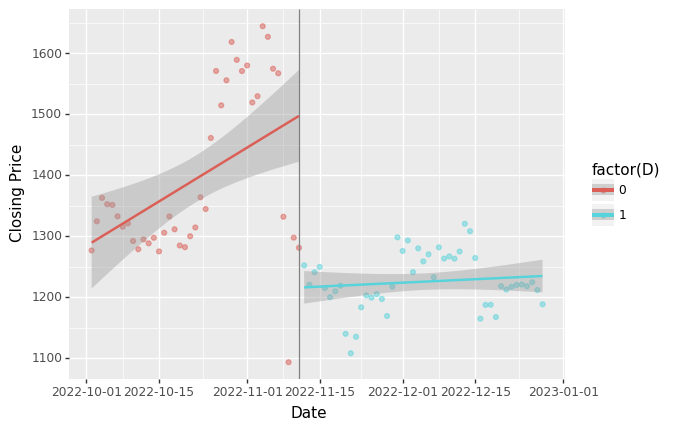
Figure 4: The causal inference result of the impact of FTX's bankruptcy on ethereum price
- Code source
- Data source
- Description: The results of the regression discontinuity analysis are presented in Figure 4, which shows a clear discontinuity in the Ethereum price following the FTX bankruptcy. The x-axis represents the date, which ranges from 2022/10/1 to 2023/1/2. The y-axis is the closing price of Ethereum. The scatter plots refer to the real closing price of Ethereum each day, and the two lines are the linear regression results of the closing price. This finding suggestes that the FTX bankruptcy had a significant causal effect on the Ethereum price. Furthermore, it indicates a gradual increase in Ethereum price over time after the event, implying that the impact of the FTX bankruptcy is likely to have diminished over time.
AI Ethics Issues
- One AI ethics issue is whether the exchange is trusted or not. The algorithms might be manipulated. For example, an exchange could potentially use tricks such as “wash trading” (i.e. buying and selling assets with oneself to create the appearance of market activity) to artificially inflate its perceived trustworthiness (Chohan 2018).
- Another issue is the manipulation of the closing price (Chohan 2018). If the algorithms used to predict the closing price of a cryptocurrency are based on incomplete or biased data, they may produce inaccurate or manipulated results that could be used to profit from insider trading or other forms of market manipulation.
More about the Author

- Self Introduction: Haowen Ji is a senior student in Data Science major at DKU, who is intereted in the data science’s application in the real world, such as price evaluation and automatic driving and still seeking more implementation opportunities to leverage data science.
- Final Reflections:
- Intellectual Growth: During this course, I grow intellectually in my understanding of the benefits of using machine learning to tackle complex social and economic issues. One of the key lessons from this course has been the importance of interdisciplinary research with peers. With the diverse perspectives and approaches brought by classmates, more effective and impactful solutions were generated.
- Professional Growth: Throughout this course, I have a great professional growth by acquiring a combination of skills and creating a professional profile that showcases my capabilities. Specifically, I have learned about cryptocurrencies, GitHub settings, academic writing, and the application of machine learning in the crypto market, which are valuable skills in today’s digital economy.
- Living a Purposeful Life: I could focus on using machine learning and causal inference techniques to develop new blockchain-based applications that can help mitigate risks and improve the stability of cryptocurrency markets. This may contribute to the future development of the cryptocurrency market, and make it the most popular market for trading. At that time, I would say that hoped everyone can join the innovation and development of new types of markets. I think for the contribution, my role is to provide accessible information and education about cryptocurrencies, as they have the potential to revolutionize the way we exchange value and conduct financial transactions.
References
Data Source
- Ethereum Historical Dataset
- Coin Metrics
Code Source
- design-principle-blockchain/code
- Rising-Stars-by-Sunshine/stats201-tutorial-prediction
- Regression_Discontinuity
Articles
- Jurisdiction of Digital Currency Part of the Commodity Market as Bankruptcy Assets in the Event of Bankruptcy under the Law in Indonesia
- Cryptocurrency Returns and Cryptocurrency Uncertainty: A Time-Frequency Analysis
- Correlation and Regression Analysis of the Relation between Ethereum Price and Both Its Volume and Bitcoin Price
- DLCP2F: A DL-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Framework
- Price Stability Using Cryptocurrency Seigniorage Shares
- Cryptocurrencies and Investment Diversification: Empirical Evidence from Seven Largest Cryptocurrencies
- The Problems of Cryptocurrency Thefts and Exchange Shutdowns
- A Survey on Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques in Bankruptcy Prediction
- A Better Coefficient of Determination for Genetic Profile Analysis
- ETHEREUM PRICE PREDICTION USING MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES – a COMPARATIVE STUDY
- LSTM-GARCH Hybrid Model for the Prediction of Volatility in Cryptocurrency Portfolios
- A Novel Hybrid Walk-Forward Ensemble Optimization for Time Series Cryptocurrency Prediction
- Survey of Natural Language Processing
- A New Grey System Approach to Forecast Closing Price of Bitcoin, Bionic, Cardano, Dogecoin, Ethereum, XRP Cryptocurrencies
- Regression Discontinuity Designs: An Introduction
- Signal Prediction in Cryptocurrency Tradeoperations: A Machine Learning-Based Approach
- Predictive Power of an Ensemble Model for Cryptocurrency Forecasting
- Price Movement Prediction of Cryptocurrencies Using Sentiment Analysis and Machine Learning
- Breaking Bitcoin: Does Cryptocurrency Exchange Activity Lead to Increased Real Activity Outside Cryptocurrency Exchanges?
- Sentiment Analysis of News for Effective Cryptocurrency Price Prediction
- SoK: Blockchain Decentralization
Literature
- Abdillah, Helmy Tsany, and Daniel Hendrawan. 2022. “Jurisdiction of Digital Currency Part of the Commodity Market as Bankruptcy Assets in the Event of Bankruptcy under the Law in Indonesia.” Journal of Administrative and Business Studies 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.20474/jabs-8.1.1.
- Ah Mand, Abdollah. 2021. “Cryptocurrency Returns and Cryptocurrency Uncertainty: A Time-Frequency Analysis.” SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3950087.
- Akbulaev, Nurkhodzha, Ilkin Mammadov, and Mehbube Hemdullayeva. 2020. “Correlation and Regression Analysis of the Relation between Ethereum Price and Both Its Volume and Bitcoin Price.” The Journal of Structured Finance, April, jsf.2020.1.099. https://doi.org/10.3905/jsf.2020.1.099.
- Aljadani, Abdussalam. 2022. “DLCP2F: A DL-Based Cryptocurrency Price Prediction Framework.” Discover Artificial Intelligence 2 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44163-022-00036-2.
- Ametrano, Ferdinando M. 2014. “Price Stability Using Cryptocurrency Seigniorage Shares.” SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2508296.
- Canh, Nguyen Phuc, Nguyen Quang Binh, and Su Dinh Thanh. 2019. “Cryptocurrencies and Investment Diversification: Empirical Evidence from Seven Largest Cryptocurrencies.” Theoretical Economics Letters 09 (03): 431–52. https://doi.org/10.4236/tel.2019.93031.
- Chohan, Usman. 2018. “The Problems of Cryptocurrency Thefts and Exchange Shutdowns.” SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3131702.
- Devi, S. Sarojini, and Y. Radhika. 2018. “A Survey on Machine Learning and Statistical Techniques in Bankruptcy Prediction.” International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing 8 (2): 133–39. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijmlc.2018.8.2.676.
- Lee, Sang Hong, Michael E Goddard, Naomi R Wray, and Peter M Visscher. 2012. “A Better Coefficient of Determination for Genetic Profile Analysis.” Genetic Epidemiology 36 (3): 214–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21614.
- Mohta, Mridul, Shanta Rangaswamy, and Monish S. 2022. “ETHEREUM PRICE PREDICTION USING MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUES – a COMPARATIVE STUDY.” International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences and Technology 7 (2): 137–42. https://doi.org/10.33564/ijeast.2022.v07i02.018.
- Moreno, Ester Aguayo, and Andres Garcia Medina. 2022. “LSTM-GARCH Hybrid Model for the Prediction of Volatility in Cryptocurrency Portfolios.” SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4132498.
- Oyewola, David Opeoluwa, Emmanuel Gbenga Dada, and Juliana Ngozi Ndunagu. 2022. “A Novel Hybrid Walk-Forward Ensemble Optimization for Time Series Cryptocurrency Prediction.” Heliyon 8 (11): e11862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11862.
- Ritchie, Graeme. 1982. “Survey of Natural Language Processing.” ACM SIGART Bulletin, no. 80 (April): 61-ff. https://doi.org/10.1145/1056176.1056184.
- Singh, Pawan Kumar, Alok Kumar Pandey, and S. C. Bose. 2022. “A New Grey System Approach to Forecast Closing Price of Bitcoin, Bionic, Cardano, Dogecoin, Ethereum, XRP Cryptocurrencies.” Quality & Quantity, July. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-022-01463-0.
- Stevens, Katrien. 2016. “Regression Discontinuity Designs: An Introduction.” Australian Economic Review 49 (2): 224–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8462.12162.
- Toledo, Jefferson de Morais, and Damires Yluska Souza. 2022. “Signal Prediction in Cryptocurrency Tradeoperations: A Machine Learning-Based Approach.” SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4062476.
- Tripathi, Manas, and Bhavya Tripathi. 2022. “Predictive Power of an Ensemble Model for Cryptocurrency Forecasting.” The Journal of Prediction Markets 16 (1). https://doi.org/10.5750/jpm.v16i1.1877.
- Valencia, Franco, Alfonso Gómez-Espinosa, and Benjamín Valdés-Aguirre. 2019. “Price Movement Prediction of Cryptocurrencies Using Sentiment Analysis and Machine Learning.” Entropy 21 (6): 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21060589.
- Vitt, David Christopher. 2013. “Breaking Bitcoin: Does Cryptocurrency Exchange Activity Lead to Increased Real Activity Outside Cryptocurrency Exchanges?” SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2371343.
- Vo, Anh-Dung. 2019. “Sentiment Analysis of News for Effective Cryptocurrency Price Prediction.” International Journal of Knowledge Engineering 5 (2): 47–52. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijke.2019.5.2.116.
- Zhang, Luyao, Xinshi Ma, and Yulin Liu. 2022. “SoK: Blockchain Decentralization.” ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2205.04256.